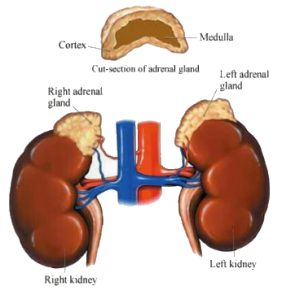
Adrenal glands, which are also called suprarenal glands, are small, triangular glands located on top of both kidneys. An adrenal gland is made of two parts: the outer region is called the adrenal cortex and the inner region is called the adrenal medulla.
Function of the adrenal glands:
The adrenal glands work interactively with the hypothalamus and pituitary gland in the following process:
- the hypothalamus produces corticotropin-releasing hormones, which stimulate the pituitary gland.
- the pituitary gland, in turn, produces corticotropin hormones, which stimulate the adrenal glands to produce corticosteroid hormones.
Both parts of the adrenal glands -- the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla -- perform very separate functions.
What is the adrenal cortex?
The adrenal cortex, the outer portion of the adrenal gland, secretes hormones that have an effect on the body's metabolism, on chemicals in the blood, and on certain body characteristics. The adrenal cortex secretes corticosteroids and other hormones directly into the bloodstream. The hormones produced by the adrenal cortex include:
- corticosteroid hormones
- hydrocortisone hormone - this hormone, also known as cortisol, controls the body's use of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates.
- corticosterone - this hormone, together with hydrocortisone hormones, suppresses inflammatory reactions in the body and also affects the immune system.
- aldosterone hormone - this hormone inhibits the level of sodium excreted into the urine, maintaining blood volume and blood pressure.
- androgenic steroids (androgen hormones) - these hormones have minimal effect on the development of male characteristics.
What is the adrenal medulla?
The adrenal medulla, the inner part of the adrenal gland, is not essential to life, but helps a person in coping with physical and emotional stress. The adrenal medulla secretes the following hormones:
- epinephrine (also called adrenaline) - this hormone increases the heart rate and force of heart contractions, facilitates blood flow to the muscles and brain, causes relaxation of smooth muscles, helps with conversion of glycogen to glucose in the liver, and other activities.
- norepinephrine (also called noradrenaline) - this hormone has little effect on smooth muscle, metabolic processes, and cardiac output, but has strong vasoconstrictive effects, thus increasing blood pressure.

0 comments:
Post a Comment